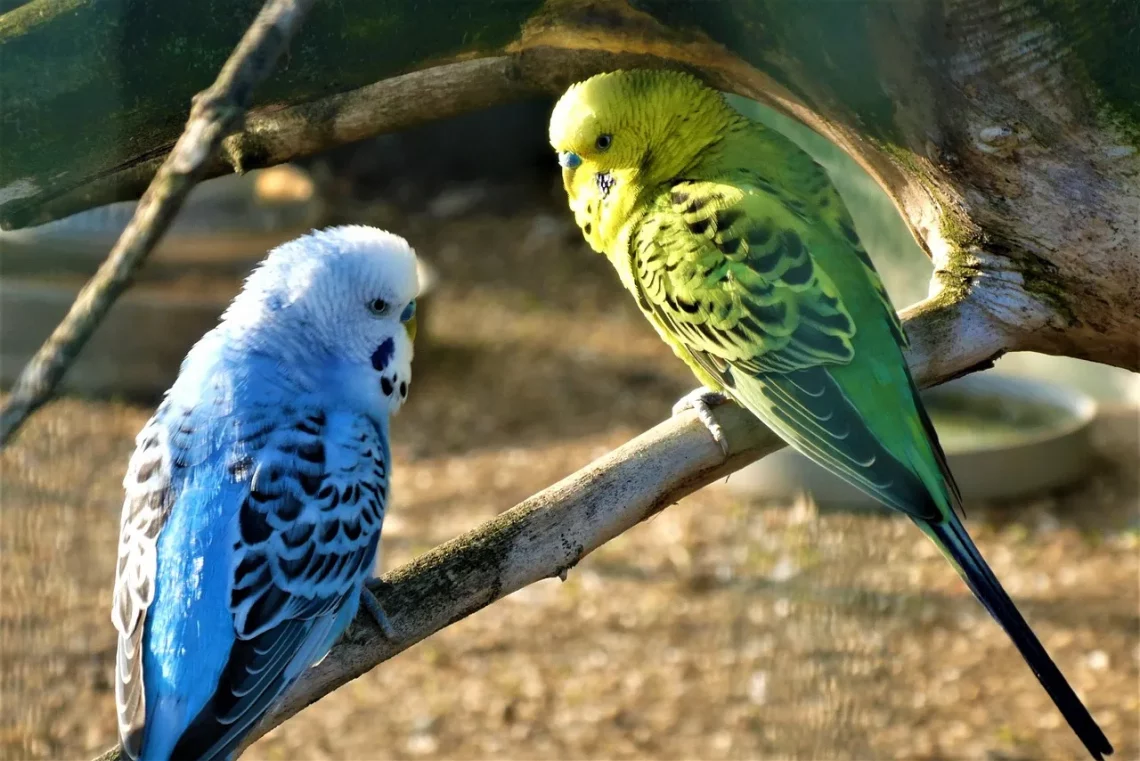
Do Parakeets Lose Tail Feathers Before Laying Eggs?
When it comes to keeping parakeets, many owners often find themselves fascinated by the various behaviors and physical changes their birds go through. These small, colorful birds are not only charming companions but also exhibit a range of natural instincts that can be intriguing to observe. One such behavior that might raise questions among parakeet enthusiasts is the shedding of tail feathers. This phenomenon can be especially concerning for those who are new to bird care or who are preparing for the breeding process.
Feather loss in parakeets can occur for various reasons, including molting, stress, or even health issues. Understanding the context in which these feathers are lost is crucial for proper care and management of these delightful pets. Many bird owners might wonder if there is a direct correlation between feather loss and the mating process, especially when it comes to laying eggs. The relationship between feather loss and reproductive behavior in parakeets is a topic that merits exploration.
In this article, we will delve into the reasons why parakeets may lose their tail feathers, particularly as they approach the breeding season. We will examine the biological processes involved, the signs of molting versus stress-related feather loss, and the implications for parakeet owners. By gaining a deeper understanding of these aspects, bird owners can better support their feathered friends during these pivotal moments.
Understanding Feather Molting in Parakeets
Feather molting is a natural process that occurs in many bird species, including parakeets. This cyclical shedding and regrowth of feathers typically happens once or twice a year. During molting, a parakeet will lose old, worn feathers to make way for new ones. This process is essential for maintaining healthy plumage, which plays a critical role in insulation, flight, and overall well-being.
Molting usually begins with the loss of primary feathers, followed by secondary feathers and tail feathers. The timing and duration of molting can vary among individual birds, often influenced by factors such as age, health, and environmental conditions. For example, seasonal changes, such as longer daylight hours in the spring and summer, can trigger molting in preparation for breeding.
During this period, parakeets may exhibit signs of discomfort, such as increased grooming or irritability. Owners may notice a few tail feathers on the cage floor, which can be alarming but is typically part of the normal molting process. It’s important to provide a stress-free environment and ensure that the bird has a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, which can support healthy feather regrowth.
Additionally, it’s crucial to differentiate between molting and feather loss caused by other factors, such as stress, illness, or dietary deficiencies. If a parakeet is losing feathers outside of the typical molting season or in large patches, it may warrant a closer examination of its health and living conditions. Regular check-ups with an avian veterinarian can help ensure that your parakeet is healthy and thriving.
Stress and Its Impact on Feather Loss
While molting is a natural and expected part of a parakeet’s life cycle, stress can also lead to feather loss, including tail feathers. Various stressors can affect parakeets, such as changes in their environment, loud noises, or the presence of predators. Additionally, aggressive behavior from other birds or even changes in routine can contribute to stress.
When a parakeet is stressed, it may engage in feather plucking or excessive preening, leading to the loss of feathers. This behavior is often a response to anxiety or discomfort and can become a habit if not addressed promptly. Stress-related feather loss is concerning because it may indicate that the bird is not coping well with its surroundings.
To mitigate stress in parakeets, owners should strive to create a calm and stable environment. This includes minimizing loud noises, providing plenty of hiding spots, and ensuring that the bird has social interaction, either with its owner or other birds. Additionally, maintaining a consistent feeding and cleaning schedule can help parakeets feel secure in their environment.
If feather loss persists despite efforts to reduce stress, it may be beneficial to consult with an avian veterinarian. They can help identify underlying health issues or recommend behavioral interventions to address stress-related behaviors.
Signs of Health Issues Related to Feather Loss
While molting and stress are common reasons for feather loss in parakeets, health issues can also play a significant role. Various medical conditions, such as infections, parasites, or nutritional deficiencies, can lead to abnormal feather loss. For instance, a parakeet suffering from a skin infection may lose feathers around the infected area, including the tail.
Common signs of health issues include changes in behavior, such as lethargy, loss of appetite, or unusual vocalizations. A bird that is ruffled or has a fluffed-up appearance may also indicate that it is unwell. If you observe any of these signs alongside feather loss, it’s crucial to seek veterinary care promptly.
Nutritional deficiencies can also lead to poor feather quality and loss. Parakeets require a balanced diet that includes seeds, pellets, fruits, and vegetables. A lack of essential nutrients, such as vitamins A, D, and E, can negatively impact feather health. Ensuring a well-rounded diet can help prevent feather-related issues and promote overall health.
In summary, while feather loss in parakeets can often be attributed to molting or stress, it is essential to remain vigilant for signs of health problems. Regular veterinary check-ups, along with a proper diet and a stress-free environment, can significantly contribute to the well-being of your feathered friend.
Preparing for Breeding: What to Expect
As parakeets approach the breeding season, their bodies undergo several changes that may include feather loss. It is essential for owners to be aware of these changes and to prepare adequately for the breeding process. During this time, females may become more active in their nesting behaviors, which can sometimes lead to the temporary shedding of tail feathers.
When a female parakeet is preparing to lay eggs, her body goes through hormonal shifts that can affect her physical condition, including feather quality. However, it’s important to note that the loss of tail feathers is not a definitive sign that a parakeet is about to lay eggs. Other behaviors, such as increased nesting activity and a more pronounced interest in mate selection, are more reliable indicators.
Providing a suitable nesting environment is crucial for breeding parakeets. This includes a comfortable nesting box and plenty of space for the birds to interact. Owners should also ensure that both male and female parakeets are in good health and have access to a balanced diet rich in calcium and protein, which are vital for egg production.
Monitoring the birds during this time is essential. Owners should be prepared for the possibility of egg-laying and understand that some parakeets may experience difficulty or health issues during this period. If any unusual behaviors or health concerns arise, it is advisable to consult an avian veterinarian for guidance.
In conclusion, while tail feather loss in parakeets can be a normal part of the molting process or a response to stress, it is crucial to remain attentive to your bird’s health and behavior, especially during breeding seasons. Creating a supportive and healthy environment will help ensure that your parakeets thrive.
**Disclaimer:** This article is not intended as medical advice. If you have concerns about your parakeet’s health or well-being, please consult a qualified veterinarian for professional guidance.